What happens when calcium carbonate reacts with water?
Calcium carbonate is a pretty stable compound, and it doesn’t really dissolve in water. It’s like trying to mix sand and water—they’ll stay separate. But, things get interesting when we introduce an acid to the mix!
When calcium carbonate reacts with an acid (like hydrochloric acid), carbon dioxide gas is released, and the resulting calcium salt is usually soluble in water. This is the reaction you’re likely thinking about:
Calcium carbonate + Acid → Calcium salt + Water + Carbon dioxide
For instance, if we mix calcium carbonate with hydrochloric acid, we get:
Calcium carbonate + Hydrochloric acid → Calcium chloride + Water + Carbon dioxide
So, while calcium carbonate doesn’t dissolve in water alone, it can react with acids to form soluble salts and release carbon dioxide. This is why you might see fizzing when you put calcium carbonate, like chalk or limestone, into an acidic solution.
Let’s dive a little deeper into why this reaction happens. The calcium carbonate molecule is made up of calcium ions (Ca²⁺) and carbonate ions (CO₃²⁻). When an acid is introduced, the hydrogen ions (H⁺) from the acid attack the carbonate ions. This breaks down the carbonate ion into carbon dioxide and water, and the calcium ion combines with the anion from the acid to form the soluble calcium salt.
This process is commonly observed in nature. For instance, caves are formed when carbon dioxide in rainwater reacts with calcium carbonate in limestone, creating soluble calcium bicarbonate. This soluble form is then carried away by the water, leaving behind the hollow cave structure.
Is calcium carbide illegal?
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has banned the use of calcium carbide for ripening fruits under the Food Safety and Standards (Prohibition and Restrictions on Sales) Regulations, 2011. This ban was implemented to protect public health.
Why is calcium carbide dangerous for ripening fruits?
When calcium carbide reacts with water, it produces acetylene gas, which is highly flammable and can cause explosions. Acetylene gas can also react with other chemicals to form toxic substances.
How does calcium carbide affect fruit?
Calcium carbide does not actually ripen fruit. It simply speeds up the process of fruit ripening by releasing ethylene gas, a natural plant hormone that is responsible for fruit ripening. However, this process is not natural and can lead to the production of fruits that are not ripe and can be harmful to human health.
What are the health risks associated with consuming fruit ripened with calcium carbide?
Fruits ripened with calcium carbide can contain high levels of toxic substances, including arsenic and phosphorus. These substances can cause a variety of health problems, including headaches, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and even cancer.
What are the alternatives to using calcium carbide for ripening fruits?
There are many safe and natural ways to ripen fruits, including storing them at room temperature, using a fruit ripening bowl, or wrapping them in newspaper. You can also use natural ripening agents such as ethylene gas, which is produced by fruits themselves during the ripening process.
It is important to choose fruits that have been ripened naturally and to avoid fruits that have been ripened with calcium carbide. By doing so, you can help to ensure your safety and the safety of your family.
What happens to calcium carbonate when it gets wet?
You might be surprised to learn that calcium carbonate doesn’t actually dissolve in plain water. It’s pretty stable. However, things get interesting when water contains dissolved carbon dioxide. Think about a raindrop falling through the air – it picks up carbon dioxide. Now, this water, slightly acidic from the carbon dioxide, can react with calcium carbonate. This reaction creates calcium bicarbonate, which is soluble in water.
So, the wetness itself doesn’t directly dissolve the calcium carbonate. It’s the presence of carbon dioxide in the water that makes the difference. This is a key process in erosion of limestone caves and formations, as well as contributing to “hard water” in some areas.
Let’s dive a little deeper into how this reaction works:
The reaction between calcium carbonate and water with dissolved carbon dioxide is a bit like a chemical dance. It’s a reversible reaction, meaning it can go both ways. When carbon dioxide is present in the water, it reacts with calcium carbonate to form calcium bicarbonate. This process removes calcium carbonate from the solid state and makes it dissolve in the water. This is what happens in nature when rainwater dissolves limestone rocks over long periods of time.
On the flip side, if the water is exposed to the air, calcium bicarbonate can decompose back into calcium carbonate, carbon dioxide, and water. This is the process that creates stalactites and stalagmites in caves. As water containing calcium bicarbonate drips from the ceiling of a cave, it’s exposed to air. Some of the carbon dioxide escapes, and calcium carbonate precipitates out of the solution, forming the stalactites.
So, in short, when calcium carbonate gets wet in the presence of carbon dioxide, it can dissolve. But, if the water loses carbon dioxide, the calcium carbonate can precipitate back out, forming new structures.
What happens when Ca reacts with H2O?
You’re right, calcium reacts with water, but it’s not as dramatic as some other metals like sodium. The reaction is less vigorous. When calcium comes into contact with water, it produces calcium hydroxide, a cloudy white substance that settles at the bottom, and hydrogen gas is released. These hydrogen gas bubbles stick to the surface of the calcium, making it float on the water.
Here’s why the reaction is less vigorous and why the bubbles stick:
Calcium’s reactivity: While calcium is a reactive metal, it’s not as reactive as metals like sodium or potassium. It reacts more slowly with water.
Calcium hydroxide formation: The calcium hydroxide produced in the reaction is slightly soluble in water. This means that some of it dissolves, making the water cloudy.
Hydrogen gas bubbles: The hydrogen gas released in the reaction forms small bubbles that stick to the calcium’s surface due to a phenomenon called surface tension. These bubbles make the calcium less dense than water, causing it to float.
It’s worth noting that, like any chemical reaction, the vigor of the reaction can be influenced by factors like the temperature of the water and the surface area of the calcium. A smaller piece of calcium will react more slowly than a larger piece, and warmer water will encourage a faster reaction.
Why does calcium react less violently with water?
Let’s delve a bit deeper into why calcium reacts less violently with water. The key lies in the reactivity of the metal, which is determined by how easily it loses electrons. Calcium is less reactive than sodium and potassium, meaning it holds onto its electrons more tightly. This makes it harder for calcium to react with water, resulting in a less vigorous reaction. You can think of it like this: calcium is like a shy person who takes their time to open up, while sodium and potassium are like outgoing folks who jump right into things.
The heat produced during the reaction is directly related to the energy released when the metal loses its electrons. Since calcium is less reactive, it releases less energy when reacting with water. This translates to less heat generated, which in turn makes it harder for the hydrogen gas to ignite. The lack of ignition is a major factor in why the reaction is less violent.
Think of it like a campfire. A small piece of wood will produce less heat than a large log. Similarly, calcium, being less reactive, releases less heat, making the reaction less energetic and less prone to causing a sudden burst of flames. This is the reason why calcium’s reaction with water is much gentler compared to the explosive reactions of sodium and potassium with water.
Why are metals so reactive with water?
Textbooks often describe the metal-water reaction in a simple way: When water interacts with a metal, the metal releases electrons. These negatively charged particles generate heat as they leave the metal. This heat, combined with the released electrons, breaks apart the water molecules.
But let’s unpack this a bit further. Metals tend to be reactive with water because they readily donate electrons. This is because they have loosely bound electrons in their outer shell, making them eager to participate in chemical reactions. This characteristic, known as electronegativity, plays a crucial role in determining a metal’s reactivity.
Metals with low electronegativity, like sodium and potassium, are very reactive with water. Their electrons are easily released, leading to a vigorous reaction that generates hydrogen gas and heat, sometimes even an explosion! Metals with higher electronegativity, like iron and aluminum, react more slowly with water, but they can still corrode over time. This happens because the reaction with water forms metal oxides, which are like rust.
Think of it like a dance: The metal, with its loose electrons, is eager to share, while the water molecule, with its own electron configuration, is looking for stability. When they meet, the electrons from the metal jump ship to the water molecule, causing a chain reaction. This reaction creates energy in the form of heat, and it also produces hydrogen gas, which is what causes the bubbling you often see when metals react with water.
So, the next time you see a metal reacting with water, remember that it’s not just a simple process of one thing hitting another. It’s a complex interplay of electrons, energy, and chemical bonds.
See more here: What Happens When Calcium Carbide Gets Wet? | Why Does Calcium Carbide React With Water
What happens when calcium carbide reacts with water?
This reaction is also exothermic, meaning it releases heat. Think of it like a mini explosion!
The chemical equation for this reaction looks like this:
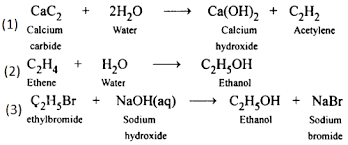
CaC₂ + 2H₂O → C₂H₂ + Ca(OH)₂
Here’s a breakdown of what’s happening:
Calcium carbide (CaC₂) reacts with water (H₂O).
* This produces acetylene gas (C₂H₂), which is what gives it that ether-like smell.
* It also creates calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂), which is a white solid.
Now, let’s dive a little deeper into why acetylene is so important. It’s a very versatile gas used in a wide range of applications, including:
Welding and Cutting:Acetylene burns with a very hot flame, making it ideal for cutting and welding metals.
Lighting:Acetylene was once used in lamps and lanterns, before being replaced by more efficient lighting sources.
Chemical Synthesis:Acetylene is a key ingredient in the production of many chemicals, including plastics and pharmaceuticals.
You can see why understanding the reaction between calcium carbide and water is important, because it’s the foundation for creating such a useful substance!
How does calcium carbide interact with oxygen?
Calcium carbide is a reactive substance that readily interacts with various elements. Besides oxygen, it also reacts with nitrogen, phosphorus, chlorine, and arsenic under specific conditions. But for now, let’s focus on its interaction with oxygen.
The reaction between calcium carbide and oxygen is an exothermic reaction, meaning it releases heat. This is because the formation of calcium carbonate is a more stable configuration than calcium carbide, and the energy difference is released as heat.
Think of it like building a sandcastle: you put in energy to make it, but it’s more stable once it’s built. The difference in energy between the sandcastle and the loose sand is released as heat, potentially making your hands warm. Similarly, the energy difference between calcium carbide and calcium carbonate is released as heat when they react.
Now, let’s delve a little deeper into this reaction. Calcium carbide (CaC₂) reacts with oxygen (O₂) in the presence of heat to form calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) and carbon dioxide (CO₂). The chemical equation for this reaction is:
“`
2CaC₂ + 5O₂ → 2CaCO₃ + 2CO₂
“`
This reaction is highly exothermic, and the heat generated can cause the calcium carbonate to decompose back into calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO₂). This is why you might see some white powder (calcium oxide) along with some gas (carbon dioxide) when calcium carbide reacts with oxygen.
This reaction is crucial in various industries, including the production of acetylene gas, which is used for welding and cutting metal. The reaction also plays a role in the manufacturing of synthetic fertilizers.
So, in a nutshell, calcium carbide and oxygen readily react when exposed to heat, producing calcium carbonate and releasing energy in the form of heat. This reaction is fundamental to several industrial processes and highlights the versatility of this unique chemical compound.
See more new information: countrymusicstop.com
Why Does Calcium Carbide React With Water? The Science Explained
What’s the science behind it?
Calcium carbide is a chemical compound made up of calcium and carbon. It’s kind of like a tiny, hard rock that’s made of those two elements. Now, water is H2O, you know, two hydrogen atoms and an oxygen atom. When they get together, they’re like two partners in a chemical dance.
The thing is, calcium carbide (CaC2) really likes to react with water (H2O). It’s kind of like a match and a spark. They just want to get together and change. The reaction between calcium carbide and water is a chemical reaction that produces acetylene gas (C2H2) and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), which is also known as slaked lime.
Let me show you what that looks like in a chemical equation:
CaC2 + 2H2O → C2H2 + Ca(OH)2
How does the reaction work?
When water molecules come into contact with calcium carbide, they break apart. Remember, water is made of hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen atoms break away from the water molecule and attach themselves to the carbon atoms in the calcium carbide. This forms acetylene gas, which is what makes that fizzing sound.
At the same time, the oxygen atoms from the water combine with the calcium from the calcium carbide to form calcium hydroxide. That’s the white powdery stuff you might see floating around after the reaction.
Why is acetylene gas so important?
Acetylene gas is highly flammable, so it’s used as fuel in welding and cutting torches. It’s a very efficient fuel, producing a very hot flame. You might even have seen those welding torches in action if you’ve ever watched a construction project.
What’s the deal with calcium hydroxide?
Calcium hydroxide is a basic compound, which means it has a pH greater than 7. It’s used in many applications like:
Construction: It’s used in the production of cement and mortar.
Agriculture: It’s used to neutralize acidic soil and improve crop yields.
Water treatment: It helps to remove impurities from water.
Important Safety Precautions
Calcium carbide and water are both dangerous if not handled properly. Here are some things you need to remember:
Acetylene gas is flammable and explosive. Never use calcium carbide in a confined space without proper ventilation.
Calcium carbide can cause burns. Always wear gloves and protective eyewear when handling it.
Calcium hydroxide is a strong base. It can irritate your skin and eyes.
FAQs
What happens if you mix calcium carbide with water?
* It reacts to produce acetylene gas and calcium hydroxide.
What is the chemical reaction that occurs when calcium carbide reacts with water?
* The reaction is CaC2 + 2H2O → C2H2 + Ca(OH)2.
Is calcium carbide dangerous?
* Yes, calcium carbide is dangerous if not handled properly. It can cause burns and fires.
What is acetylene gas used for?
* Acetylene gas is used in welding and cutting torches.
What is calcium hydroxide used for?
* Calcium hydroxide is used in construction, agriculture, and water treatment.
Final thoughts
It’s always fascinating to see how everyday things can react in unexpected ways, like calcium carbide and water. It’s a good reminder that there’s a lot of chemistry happening all around us, even in the simplest things. Just remember to handle things with care and respect those chemical reactions, especially the flammable ones!
Calcium carbide and Water Reaction | CaC2 + H2O
Calcium carbide (CaC2) hydrolysis and react in the water to give acetylene (C2H2), calcium hydroxide. This reaction is used to prepare acetylene gas in the laboratory. A white precipitated Ca(OH)2 is formed in this reaction. chemistryscl.com
Chemical characteristics of calcium carbide and its reaction with
Calcium carbide is not volatile and not soluble in any known solvent, and reacts with water to yield acetylene gas and calcium hydroxide. Its density is 2.22 g/cm³. Its melting point MEL Science
Calcium Carbide – Structure, Properties, and Uses of CaC2
Calcium carbide can be reacted with water to produce acetylene and calcium hydroxide. Calcium cyanamide can also be produced from this compound by BYJU’S
Reaction of Calcium Carbide [CaC2] with water – YouTube
Many people know the reaction of calcium carbide with water, because the highly flammable ethyne gas is often used as a “safe” explosive to play with. YouTube
Is the reaction of calcium carbide with water a Brønsted-Lowry
We may regard the calcium hydroxide and calcium carbide as essentially ionic except for the covalent bonding within the anions. So there is no Lewis reaction involving the Chemistry Stack Exchange
Write the chemical reaction for the Calcium carbide and water
The reaction between Calcium carbide and water: Calcium carbide ( CaC 2 ) reacts with Water ( H 2 O ) to produce colorless gas with an Ether-like odor known as Acetylene gas BYJU’S
Hydrolysis of calcium carbide and characteristics of
At high temperatures, calcium carbide enters into a reaction with phosphorous, chlorine and arsenic. One of the most important properties of the substance is the breakdown by water. Calcium carbide is MEL Science
reactions between metals and water or steam – chemguide
Calcium’s reaction with water is similar to lithium’s. It looks a bit different because calcium is denser than water and so sinks. The first bit of video shows quite a large chunk of chemguide
23.5: Carbon, Carbides, and Carbonates – Chemistry LibreTexts
The lamp uses burning acetylene, produced by the slow reaction of calcium carbide with water, to provide light. The reaction of carbon with most transition metals at high Chemistry LibreTexts
Calcium Carbide And Water Reaction – Combustion Reaction Of Acetylene
Calcium Carbide And Water \U0026 Combustion Of Acetylene
What Happens When Calcium Carbide Is Allowed To React With Water .
What Happens When You Mix Calcium Carbide With Water?
Calcium Carbide Reacts With Water To Produce Acetylene
Link to this article: why does calcium carbide react with water.
See more articles in the same category here: blog https://countrymusicstop.com/wiki
