Are purple flowers dominant over white flowers in a pea plant?
A single gene controls this trait in Mendel’s pea plants. This means that there’s one specific gene that determines whether a pea plant will have purple or white flowers. We can think of the gene as having two different versions, or alleles: one for purple (P) and one for white (p).
Now, there are three possible combinations of these alleles:
PP: This combination has two copies of the purple allele. A plant with this genotype will have purple flowers.
Pp: This combination has one copy of the purple allele and one copy of the white allele. Even though it has the white allele, the purple allele is dominant, meaning it masks the effect of the white allele. So, a plant with this genotype will also have purple flowers.
pp: This combination has two copies of the white allele. Since there’s no dominant purple allele present, a plant with this genotype will have white flowers.
It’s important to understand that the term “dominant” doesn’t mean the purple allele is “better” or more powerful than the white allele. It simply means that the purple allele is expressed even when the white allele is present. This is why plants with the Pp genotype have purple flowers, even though they carry the white allele.
Now, let’s dive a bit deeper into how this works. You might be asking, “How does a plant with two copies of the white allele (pp) end up with white flowers?”
The answer lies in how genes work. Genes provide instructions for making proteins. Proteins are the workhorses of the cell, carrying out a wide range of functions. In this case, the gene responsible for flower color provides instructions for making a protein that produces pigment.
The P allele instructs the plant to make a functional pigment protein, resulting in purple flowers. The p allele, however, has a mutation that prevents it from making a functional pigment protein. So, a plant with the pp genotype doesn’t make any pigment protein, resulting in white flowers.
Understanding how dominance works in this example can help you understand how genes and alleles control other traits in plants and animals. It’s fascinating how a single gene can have such a significant effect on the appearance of an organism!
Which is dominant in pea plant violet or white?
To understand this better, let’s delve into the world of genetics. Each pea plant inherits two genes for flower color, one from each parent. These genes come in two forms called alleles: the purple allele (represented as “P”) and the white allele (represented as “p”).
A purple-flowered plant can have either two purple alleles (PP) or one purple and one white allele (Pp). Both of these combinations will result in purple flowers. This is because the purple allele is dominant, so even if the plant has one white allele, the purple allele will still determine the flower color.
A white-flowered plant can only have two white alleles (pp). This is because the white allele is recessive, meaning it can only be expressed if the plant has two copies of the white allele.
When you cross a purple-flowered plant (PP or Pp) with a white-flowered plant (pp), you can predict the offspring’s flower colors using a Punnett square. The Punnett square is a visual tool that helps us understand the probability of different combinations of alleles being passed down from parents to offspring.
Here’s how it works:
Parent 1: Purple-flowered plant (Pp)
Parent 2: White-flowered plant (pp)
| | p | p |
|——-|——-|——-|
| P | Pp | Pp |
| p | pp | pp |
As you can see, all the offspring have at least one purple allele (P), which means they will all have purple flowers. This demonstrates how purple flower color is dominant over white flower color in pea plants.
What is the dominant flower position in pea plant?
Let’s break down what this means in more detail:
Axial flowers grow along the stem of the plant, whereas terminal flowers grow at the tip of the stem.
Dominant genes are those that are more likely to be expressed in an organism’s traits, while recessive genes are only expressed if the organism inherits two copies of the recessive gene.
* When a plant inherits one axial gene and one terminal gene, the axial gene will be expressed, and the plant will have axial flowers.
Understanding dominant and recessive genes is a fundamental concept in genetics. It helps us understand how traits are passed down from generation to generation. In the case of pea plants, knowing the dominant flower position allows us to predict the flower position of offspring based on the parental genes.
For example, if a pea plant with axial flowers (Aa) is crossed with a pea plant with terminal flowers (aa), the offspring will have a 50% chance of inheriting the axial gene and a 50% chance of inheriting the terminal gene. Therefore, half of the offspring will have axial flowers and half will have terminal flowers.
What does “purple flowers are dominant to white flowers” mean?
Imagine a plant with two genes for flower color – one from its “mom” and one from its “dad”. These genes are called alleles, and they carry the instructions for color.
Now, if one allele tells the plant to make purple flowers and the other allele tells it to make white flowers, the plant will have purple flowers.
Why? Because the purple flower allele is dominant. It “masks” the effect of the white flower allele, which is considered recessive.
Think of it like a tug of war. The dominant allele (purple) is stronger and wins, so the plant shows the dominant trait. The recessive allele (white) is there, but its effect is hidden.
This is why, in the F2 generation of 400 plants, it’s expected that only 100 of them would be genotypically homozygous for white flowers. The remaining 300 would have at least one purple allele, making their flowers purple.
To understand this further, let’s delve into genotypes and phenotypes. A genotype represents the actual combination of alleles a plant has. For example, a plant with one purple allele and one white allele would have the genotype Pp. A plant with two purple alleles would have the genotype PP, and a plant with two white alleles would have the genotype pp.
Phenotype, on the other hand, refers to the physical trait that is expressed. In our case, the phenotype is the flower color. A plant with the genotypes PP or Pp will have purple flowers because the purple allele is dominant. A plant with the genotype pp will have white flowers because it has two copies of the recessive allele.
The concept of dominant and recessive alleles is fundamental to understanding how traits are inherited and passed down through generations. It explains why some traits appear more often than others, and it lays the foundation for more complex genetic concepts.
Why does a pea plant have purple flowers?
A mutation in the A gene can cause a plant to produce white flowers. This mutation prevents the protein from being produced correctly, which means it can’t turn on the genes for anthocyanin synthesis.
The A gene is just one of many genes that contribute to flower color. Other genes also influence the production of pigments and the way those pigments are displayed in the petals. These genes work together to create the wide range of colors we see in pea plants and other flowering plants.
The A gene is a fascinating example of how genes control complex traits. Understanding the role of this gene helps us appreciate the beauty and diversity of the natural world. It’s like a tiny blueprint that tells the pea plant what color to be!
Is white dominant or recessive in pea plant?
On the other hand, white flowers are a recessive trait. For a pea plant to have white flowers, it needs to inherit two copies of the gene for white flowers, one from each parent. If it inherits even one gene for violet flowers, it will have violet flowers.
Think of it like this: violet is like a strong personality that always shows up. White is like a shy personality that only shows up if there’s no one else to take center stage.
Here’s an example:
Let’s say you have two pea plants. One has violet flowers and one has white flowers. The violet flower plant has one gene for violet flowers and one gene for white flowers. The white flower plant has two genes for white flowers.
If these two plants have offspring, the offspring will inherit one gene from each parent. They could inherit the gene for violet flowers from the violet flower parent and the gene for white flowers from the white flower parent. Since violet flowers are dominant, these offspring will have violet flowers.
However, there’s a chance that the offspring will inherit two genes for white flowers, one from each parent. In this case, the offspring will have white flowers.
This is why white flowers are recessive. They only show up if the plant inherits two copies of the gene for white flowers.
What are the 4 dominant traits of pea plants?
These are the four dominant traits Mendel focused on:
Pea shape:Round peas are dominant over wrinkled peas.
Pea color:Yellow peas are dominant over green peas.
Pod shape:Inflated pods are dominant over constricted pods.
Pod color:Green pods are dominant over yellow pods.
Now, let’s dive a little deeper into these traits:
Pea Shape:
The shape of the pea is determined by the presence or absence of a specific enzyme that helps starch production. Round peas have this enzyme and can store starch. Wrinkled peas lack the enzyme, so they store sugar instead. This difference in storage leads to the wrinkled appearance.
Pea Color:
The color of the pea is determined by the presence or absence of a pigment called chlorophyll. Yellow peas lack this pigment, while green peas have it.
Pod Shape:
The shape of the pod is determined by the development of the reproductive cells. Inflated pods have a smooth, continuous surface. Constricted pods have indentations between the seeds, making them look pinched.
Pod Color:
The color of the pod is similar to the pea color. Green pods contain chlorophyll, while yellow pods lack it.
Understanding these dominant traits in pea plants helped Mendel develop his laws of inheritance, which are still fundamental to our understanding of genetics today.
Why yellow is dominant in pea plant?
Yellow peas have a gene, which we call Y, that’s dominant over the recessive green gene, y. This means that if a pea plant inherits even just one copy of the Y gene from either parent, it will produce yellow peas.
Think of it like this: imagine the Y gene is a loud, bossy voice, and the y gene is a quiet whisper. Even if the plant has both genes, the Y gene’s voice always overshadows the y gene’s whisper.
How this works in practice:
When a pea plant makes seeds, it only gives one copy of its color gene to each seed. So if a plant has the YY combination (two copies of the Y gene), all its seeds will also be YY, resulting in yellow peas.
But things get interesting when a plant has the Yy combination (one Y and one y gene). In this case, the plant still produces yellow peas because the Y gene is dominant. It’s only when a plant inherits two copies of the recessivey gene (yy) that it will produce green peas.
The key takeaway: A pea plant needs to inherit two copies of the y gene to produce green peas. If it has even one copy of the Y gene, it will produce yellow peas.
Which color of pea is dominant?
Let’s talk about seed color. Yellow is the dominant trait, meaning that if a pea plant inherits even one gene for yellow seeds, it will produce yellow seeds. Green is recessive. This means that a pea plant will only produce green seeds if it inherits two genes for green seeds.
Now, let’s shift gears to pod color. Things get a bit flipped here! Green is the dominant trait for pod color. So, a pea plant will have green pods if it inherits at least one gene for green pods. Yellow is the recessive trait, meaning a pea plant will only have yellow pods if it inherits two genes for yellow pods.
To understand this better, let’s imagine a pea plant that inherits one gene for yellow seeds and one gene for green seeds. Since yellow is dominant, the pea plant will produce yellow seeds. But what about its pods? If it inherits one gene for green pods and one gene for yellow pods, it will produce green pods. This is because green is the dominant trait for pod color.
This concept of dominant and recessive traits is fundamental to understanding how traits are passed down from one generation to the next. Gregor Mendel, the father of genetics, discovered these principles through his work with pea plants. He meticulously studied the different traits of pea plants, including seed color, pod color, and flower color, and realized that these traits are passed down in predictable patterns. His work laid the foundation for our understanding of genetics, which continues to be an area of intense research and discovery today.
See more here: Which Is Dominant In Pea Plant Violet Or White? | In Pea Plants Purple Flowers Are Dominant Over White Flowers
Are purple flowers dominant over white flowers in garden peas?
Now, imagine we cross two purple-flowered plants. They produce 324 purple-flowered offspring and 103 white-flowered offspring. How can we figure out the genetic makeup of the parent plants?
Let’s break it down:
Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism, represented by letters.
Phenotype: The physical characteristics of an organism.
Since white flowers are recessive, a plant needs two copies of the white flower gene to display white flowers. This tells us that the 103 white-flowered offspring must have received a white flower gene from each parent.
To produce a white flower offspring, both parent plants must have at least one white flower gene. The most likely scenario is that one parent is heterozygous (carrying one purple flower gene and one white flower gene) and the other parent is homozygous recessive (carrying two white flower genes).
Let’s look at the Punnett square for this scenario:
| | P | p |
|——-|——-|——-|
| p | Pp | pp |
| p | Pp | pp |
This shows that the offspring could have a Pp genotype (purple flowers) or a pp genotype (white flowers). This matches our observed ratio of purple to white offspring.
Now let’s explore a scenario with a homozygous purple plant and a homozygous white plant.
A homozygous purple plant has two purple flower genes (PP). A homozygous white plant has two white flower genes (pp).
Let’s look at their Punnett square:
| | P | P |
|——-|——-|——-|
| p | Pp | Pp |
| p | Pp | Pp |
In this case, all the offspring (100%) will be heterozygous with the genotype Pp and therefore have purple flowers.
Understanding the inheritance of these flower colors is a foundational concept in genetics, illustrating the power of dominant and recessive traits in shaping the characteristics of offspring!
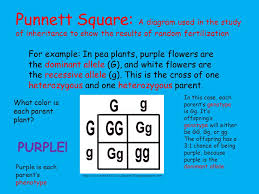
Are two pea plants heterozygous for purple flowers?
Imagine we have two pea plants that are heterozygous for purple flowers. This means each plant has one purple flower allele and one white flower allele. If we cross these two plants, what are the chances their offspring will have white flowers?
To figure this out, we can use a Punnett square. This is a simple tool that helps us visualize the possible combinations of alleles that the offspring can inherit.
| | P | p |
| ——– | —— | —— |
| P | PP | Pp |
| p | Pp | pp |
In this Punnett square, P represents the purple flower allele and p represents the white flower allele. As you can see, there are four possible combinations of alleles for the offspring: PP, Pp, Pp, and pp.
PP and Pp both result in purple flowers because the purple flower allele is dominant.
pp results in white flowers because there is no purple flower allele to mask the white flower allele.
This means that there is a 1 in 4 chance, or 25%, that the offspring will have white flowers. And there is a 3 in 4 chance, or 75%, that the offspring will have purple flowers.
The example you mentioned, where 324 purple and 103 white plants were produced, is very close to these theoretical probabilities. This is because the more offspring we have, the closer the actual results will be to the expected probabilities.
Now, let’s address the question of how many of the 100 seeds would be white. Since there’s a 1 in 4 chance of a seed growing into a white flower, we’d expect about 25 of the seeds to produce white flowers (100 seeds * 0.25 = 25 seeds). Of course, this is just an estimate, and the actual number of white flowers could vary slightly.
This is a great example of how understanding the basics of genetics can help us predict the traits of offspring. It’s a fun way to explore the world around us and see how nature works at the most fundamental level!
Which colour is dominant in a pea plant?
Now, if you take those offspring, which are all purple, and you let them self-pollinate, you’ll see a mix of colors in the next generation. This is because the white gene is still present, even though it’s not expressed in the first generation.
Here’s how it breaks down:
Pure purple plant (PP) x Pure white plant (pp) = All purple offspring (Pp). Since purple is dominant, all plants will have purple flowers even though they carry one purple allele (P) and one white allele (p). These plants are called heterozygous for flower color.
Heterozygous purple plant (Pp) x Heterozygous purple plant (Pp) = Purple and white offspring. When these plants self-pollinate, there’s a 3:1 ratio of purple to white offspring.
This means that 75% of the plants will have purple flowers and 25% will have white flowers. You can see this pattern in the Punnett square, which is a handy tool for predicting the possible offspring of a cross.
The purple color is dominant because the gene that produces purple pigment is more powerful than the gene that produces white pigment. This means that even if a plant has both the purple and white genes, it will still have purple flowers because the purple gene is dominant. This is a classic example of Mendelian inheritance, a fundamental principle in genetics.
Understanding how these genes work helps us understand how traits are passed down from generation to generation, and this knowledge is essential for breeding crops and studying the evolution of species.
What color is a purple pea plant?
We’ll look at a cross between two pea plants: PpYY and ppYy. The first plant has one purple flower gene (P) and one white flower gene (p), and two yellow pea genes (YY). The second plant has two white flower genes (pp) and one yellow pea gene (Y) and one green pea gene (y).
To figure out the possible genotypes (the combination of genes) and phenotypes (the physical traits) of their offspring, we need to use a Punnett square. Let’s break down how this works:
Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism. For example, PpYY is the genotype of the first parent plant.
Phenotype: The physical expression of the genotype. For example, purple flowers and yellow peas is the phenotype of the first parent plant.
Let’s build our Punnett square! We’ll write the genotype of the first parent plant across the top and the genotype of the second parent plant down the side:
| | pY | py |
|———-|———–|———–|
| PpYY | PpYy | PpYy |
| PpYY | PpYy | PpYy |
Each box in the Punnett square represents a possible genotype of the offspring.
Now, let’s look at the phenotypes that each genotype represents:
PpYy:Purple flowers and yellow peas
PpYy:Purple flowers and yellow peas
PpYy:Purple flowers and yellow peas
PpYy:Purple flowers and yellow peas
As you can see, all possible offspring from this cross will have purple flowers and yellow peas.
Why? Because each offspring inherits at least one P gene for purple flowers and at least one Y gene for yellow peas. The p and y genes are recessive, meaning they only show up if there’s no dominant gene present.
So, the possible genotypes of the offspring are all PpYy, and the possible phenotype is purple flowers and yellow peas.
Here’s a little more about how the purple flower trait works:
Purple flowers are dominant to white flowers.
* This means that a plant with at least one purple flower gene (P) will have purple flowers.
* If a plant has two white flower genes (pp), it will have white flowers.
It’s all about the power of dominant genes!
See more new information: countrymusicstop.com
In Pea Plants Purple Flowers Are Dominant Over White Flowers: Understanding Mendelian Genetics
It’s kind of like a power struggle, and the purple flower gene is the boss. It’s all about genetics and how genes are passed down from parents to offspring.
Dominant & Recessive Traits
We’re talking about dominant and recessive traits. Let me break it down:
Dominant traits are like the strong, bossy genes. They show up in the offspring even if they only got one copy of that gene from their parents. Think of it like having a super power that always comes through.
Recessive traits are like the shy, quiet genes. They only show up if the offspring gets two copies of that gene, one from each parent.
In our pea plant example, the purple flower gene is dominant. So, if a pea plant inherits at least one copy of the purple flower gene, it’ll have purple flowers.
But what about the white flower gene? Well, that’s the recessive one. A pea plant needs two copies of the white flower gene to actually have white flowers.
Gregor Mendel’s Experiments
Let’s go back in time to the 1800s. A dude named Gregor Mendel (the “father of genetics”) was messing around with pea plants and noticed this whole dominance thing.
He figured out that traits, like flower color, were passed down from parents to offspring. He called these traits “factors” which we now call genes.
And guess what? He also discovered that these genes come in pairs – one from mom and one from dad.
Punnett Squares: The Genetic Blueprint
To understand how dominant and recessive traits play out, we use a tool called a Punnett square.
Imagine you have two pea plants. One has purple flowers and one has white flowers. They’re going to have a little pea plant baby.
Plant 1: Let’s say its genes are PP (two dominant purple flower genes).
Plant 2: Its genes are pp (two recessive white flower genes).
Now, we draw a Punnett square to figure out what the baby pea plant’s flowers will be like.
| | P | P |
|——-|——–|———|
| p | Pp | Pp |
| p | Pp | Pp |
* The baby pea plant will inherit one gene from each parent.
* In this case, all the possible combinations lead to Pp, which means the baby pea plant will have purple flowers!
This is because the purple flower gene (P) is dominant.
Other Traits in Pea Plants
Flower color isn’t the only thing Mendel looked at. He also studied other pea plant traits, like:
Seed Shape: Round seeds are dominant over wrinkled seeds.
Seed Color:Yellow seeds are dominant over green seeds.
Pod Shape: Inflated pods are dominant over constricted pods.
Pod Color:Green pods are dominant over yellow pods.
Stem Height: Tall stems are dominant over short stems.
He saw the same pattern – dominant traits are expressed even with one copy of the gene, while recessive traits need two copies.
Understanding Genetics
Mendel’s pea plant experiments were groundbreaking. They helped us understand how genes work and how traits are passed down through generations. This knowledge is crucial in fields like:
Medicine: Understanding genetic disorders and how to treat them.
Agriculture: Developing new crops with desirable traits.
Evolutionary Biology: Understanding how species change over time.
FAQs
#1. What happens if a pea plant inherits one purple flower gene and one white flower gene?
If a pea plant inherits one purple flower gene (P) and one white flower gene (p), it will have purple flowers. The purple flower gene is dominant, so it overpowers the white flower gene.
#2. How can a pea plant with white flowers have a baby pea plant with purple flowers?
This can happen if both parent pea plants carry the recessive white flower gene. Let’s say each parent has the genes Pp. They both have purple flowers, but they are also carrying the recessive white flower gene.
Here’s a Punnett square showing this:
| | P | p |
|——-|——–|———|
| P | PP | Pp |
| p | Pp | pp |
There’s a 1 out of 4 chance that the baby pea plant will inherit two recessive white flower genes (pp), which would give it white flowers. The other three combinations would result in purple flowers.
#3. Can I see Mendel’s pea plants in real life?
Sadly, you can’t. Mendel’s pea plants are long gone. But you can find similar pea plants at gardens and nurseries.
#4. Is there a way to change a pea plant’s flower color?
It’s tricky to directly change a pea plant’s flower color after it’s grown. But you can influence the color of future generations by carefully selecting which plants to breed.
#5. Can I do my own pea plant experiments?
You totally can! It’s a fun and educational way to learn about genetics. You can buy pea plant seeds online or at a garden center. Just make sure to keep track of your plants’ traits and see what happens when they reproduce.
It’s amazing how these simple pea plants have taught us so much about how life works. And who knows, maybe you’ll even make some cool discoveries of your own!
Bio lab quiz 2 Flashcards | Quizlet
In pea plants, the purple flower allele is dominant over the white flower allele. If p represents the dominant allele and q represents teh recessive allel, what are the correct Quizlet
8.2: Laws of Inheritance – Biology LibreTexts
In pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant to white (p), and yellow peas (Y) are dominant to green (y). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for a cross between PpYY and ppYy pea Biology LibreTexts
In pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant over white (p)
A pure breeding pea plant that produces purple flowers is crossed with a pure breeding pea plant that produces white flowers, and all of the offspring plants in the F1 generation Homework.Study.com
In pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant over white (p)
In pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant over white (p) flowers. Suppose a heterozygous purple plant is crossed with a homozygous purple plant. Use a Punnett Homework.Study.com
16.2: Mendel’s Experiments and Laws of Inheritance
In the F2 generation, approximately three-quarters of the plants had violet flowers, while one-quarter had white flowers. The offspring of the P generation are called the F1 (for filial, or “offspring”) generation. Biology LibreTexts
Mendel’s Laws – Mendelian Genetics – Wyzant Lessons
Mendel studied several different traits of a pea plant. For example, some pea plants have purple flowers and others have white flowers. Pea plants can either self-fertilize or cross-fertilize. Crossing two plants is called Wyzant
12.3 Laws of Inheritance – Biology for AP® Courses
In pea plants, purple flowers (P) are dominant to white flowers (p) and yellow peas (Y) are dominant to green peas (y). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for a OpenStax
BSCI 124 Lecture Notes — Mendelian Genetics – UMD
In peas, the gene for red flowers (R) is dominant over the gene for white flowers (r). A pea plant with white flowers is crossed with one that has red flowers. Of the umd.edu
5. In Pea Plants Purple Flowers Are Dominant To White Flowers. A Purple Plant With An Unknown Genot…
A Pea Plant With Purple Flowers Was Crossed With White Flowers Producing All 50 Plants
A Homozygous Purple Flower Variety Of Pea [Pp] Is Crossed With White Flower Variety Of Pea [P. A…
In Pea Plants, Purple Flowers Are Dominant To White. Complete The Chart Showing The Genotypes And P…
Gregor Mendel’S Pea Experiment
Link to this article: in pea plants purple flowers are dominant over white flowers.
See more articles in the same category here: blog https://countrymusicstop.com/wiki
