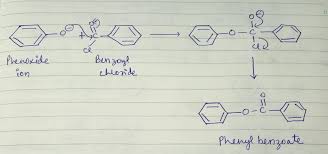
What happens when phenol reacts with benzoyl chloride?
When phenol reacts with benzoyl chloride in the presence of dilute NaOH, you get phenyl benzoate. This reaction is called benzoylation, and it’s a pretty neat way to make an ester.
Here’s the breakdown:
Phenol: Phenol is an aromatic compound with a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a benzene ring.
Benzoyl chloride: Benzoyl chloride is a reactive compound with a benzoyl group (C6H5CO-) attached to a chlorine atom.
Dilute NaOH: The dilute sodium hydroxide acts as a base, and it’s crucial for the reaction to happen.
So how does it work?
1. The sodium hydroxide reacts with phenol to form the phenoxide ion. This ion is a much stronger nucleophile than phenol itself.
2. The phenoxide ion then attacks the carbonyl carbon of benzoyl chloride. This forms a tetrahedral intermediate.
3. The tetrahedral intermediate then collapses, kicking out the chloride ion. This forms phenyl benzoate, the ester product.
The reaction is quite straightforward, but you’ll find that it’s widely used in organic chemistry. It’s a great way to introduce a benzoyl group onto a molecule, and that can be really useful for making new and interesting compounds.
Let me know if you have any other questions!
How do you synthesize benzyl benzoate?
It’s made by reacting benzoic acid with toluene in the presence of a catalyst and water. The catalyst is a special mix of metal oxides including zirconium, copper, aluminum, zinc, boron, and a rare earth element. The exact proportions of these elements are important, but you can change them a bit depending on what you’re trying to achieve.
The chemical reaction is called esterification. Benzoic acid and toluene combine to form benzyl benzoate and water. This process is usually carried out at high temperatures to speed up the reaction.
Think of it like baking a cake. You need the right ingredients (in this case, the reactants) and the right conditions (temperature, catalyst) to get the desired product (the benzyl benzoate).
Let’s dive a bit deeper into this intriguing process.
Unveiling the Catalyst’s Magic
That catalyst plays a crucial role in the benzyl benzoate synthesis. It acts like a matchmaker, bringing the benzoic acid and toluene molecules together and facilitating their reaction.
The specific composition of the catalyst can influence the reaction’s efficiency and the quality of the final product. For example, the presence of zirconium in the catalyst might promote the formation of benzyl benzoate while reducing the formation of unwanted byproducts.
The rare earth element in the catalyst adds another layer of complexity. It can influence the catalyst’s acidity, which directly affects the reaction rate. Scientists are constantly exploring different combinations of these metal oxides to improve the efficiency and sustainability of the benzyl benzoate synthesis process.
By fine-tuning the catalyst composition, we can optimize the production of this valuable compound, leading to its wider use in various applications.
When benzene react with benzoyl chloride?
Benzoyl chloride reacts with benzene in the presence of a catalyst, anhydrous aluminum chloride (AlCl3), to form benzophenone. This reaction is a classic example of Friedel-Crafts acylation.
Here’s a closer look at what’s going on:
Friedel-Crafts Acylation: This is a powerful tool in organic chemistry for adding an acyl group (R-C=O) to an aromatic ring. In this case, the acyl group comes from benzoyl chloride, which is a good source of electrophilic acylium ions.
The Role of Aluminum Chloride: Aluminum chloride acts as a Lewis acid catalyst. It coordinates with the benzoyl chloride, making the carbonyl carbon even more electrophilic. This makes it much easier for the benzene ring to attack the carbonyl carbon.
The Attack: The benzene ring acts as a nucleophile, attacking the electrophilic acylium ion. This forms a new carbon-carbon bond, adding the acyl group to the benzene ring.
Proton Transfer: After the initial attack, a proton is transferred from the newly formed carbon-carbon bond to a chloride ion, generating benzophenone and regenerating the aluminum chloride catalyst.
So, in essence, the Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene with benzoyl chloride results in the formation of benzophenone.
Think of it this way:
1. Benzoyl chloride brings the acyl group to the party.
2. Aluminum chloride acts as the matchmaker, making the acyl group more attractive to the benzene ring.
3. Benzene gets a little bit flirty and attacks the acyl group, creating a new bond.
4. A little bit of rearranging happens, and benzophenone is born.
It’s a beautiful process, right?
How to convert phenol into phenyl ethanoate?
Here’s the deal: Phenol reacts with ethanoyl chloride at room temperature to produce phenyl ethanoate and hydrogen chloride gas. While this reaction occurs, it’s not as quick as the reaction between ethanoyl chloride and a simple alcohol.
Why is that? Well, the hydroxyl group (-OH) in phenol is less reactive than the hydroxyl group in alcohols. This is due to the presence of the aromatic ring, which delocalizes the electrons in the hydroxyl group, making it less likely to participate in a nucleophilic attack. So, the reaction needs a little extra nudge to get going.
Let’s dive a bit deeper: The reaction between phenol and ethanoyl chloride is an example of esterification, a process that involves the formation of an ester. In this case, phenyl ethanoate is the ester formed.
Here’s how it works: The ethanoyl chloride acts as an electrophile, meaning it is attracted to electron-rich species like the hydroxyl group in phenol. The hydroxyl group in phenol acts as a nucleophile, meaning it is attracted to electron-deficient species like the carbonyl carbon in ethanoyl chloride.
The reaction proceeds in two steps:
1. Nucleophilic attack: The hydroxyl group in phenol attacks the carbonyl carbon in ethanoyl chloride, breaking the carbon-chlorine bond and forming a new carbon-oxygen bond.
2. Elimination of HCl: The chlorine atom, now bonded to the oxygen atom, leaves as a chloride ion (Cl-), while a proton (H+) is eliminated from the oxygen atom, forming hydrogen chloride gas.
The end result is the formation of phenyl ethanoate, a sweet-smelling liquid used in various applications, including perfumes and flavors.
Let’s wrap it up: The conversion of phenol to phenyl ethanoate is a fascinating reaction that showcases the reactivity of different functional groups. Understanding the nuances of these reactions helps us grasp the fundamental principles of organic chemistry.
What is the formula for phenyl benzoate?
C13H10O2 is the chemical formula for phenyl benzoate. This formula tells us the exact number of each atom present in a molecule of phenyl benzoate: 13 carbon atoms, 10 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms.
Phenyl benzoate is an organic compound that is an ester derived from benzoic acid and phenol. It’s a white crystalline solid that’s often used in perfumes and cosmetics due to its pleasant odor.
But how do we arrive at that formula? Well, it’s all about understanding the structure of the molecule. Phenyl benzoate is formed by the reaction between benzoic acid and phenol, with the elimination of a water molecule. This reaction is called esterification.
The benzoate part of the name comes from benzoic acid, a simple aromatic carboxylic acid with the formula C7H6O2. The phenyl part comes from phenol, a simple aromatic compound with the formula C6H6O.
When benzoic acid and phenol react, the -OH group from the benzoic acid and a hydrogen atom from the phenol are removed, forming water (H2O). The remaining fragments then combine to form phenyl benzoate, giving it the formula C13H10O2.
Understanding this process helps you see how the chemical formula of phenyl benzoate is derived and what its structure looks like. The formula C13H10O2 represents the building blocks of this important compound.
How will you prepare benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol?
Here’s how it works:
The hydroxide ion attacks the carbon atom attached to the chlorine atom in benzyl chloride. This causes the chlorine atom to leave as a chloride ion.
The hydroxide ion then bonds to the carbon atom, forming benzyl alcohol.
The reaction can be represented by the following chemical equation:
C6H5CH2Cl + KOH → C6H5CH2OH + KCl
Let’s break down this reaction in more detail:
Benzyl chloride is an aromatic compound with a chlorine atom attached to the benzene ring.
Potassium hydroxide is a strong base and provides the hydroxide ions for the reaction.
Benzyl alcohol is an aromatic alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to the benzene ring.
Potassium chloride is a salt that is formed as a byproduct.
Why does this work?
The carbon atom in benzyl chloride is attached to a chlorine atom which is a good leaving group. This means that the chlorine atom is easily removed from the molecule. The hydroxide ion is a strong nucleophile, which means that it is readily attracted to the positively charged carbon atom. These factors make the reaction favorable and allow us to easily convert benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol.
See more here: What Happens When Phenol Reacts With Benzoyl Chloride? | Reaction Of Phenol With Benzoyl Chloride To Give Phenyl Benzoate
See more new information: countrymusicstop.com
Reaction Of Phenol With Benzoyl Chloride To Give Phenyl Benzoate | How Do You Synthesize Phenyl Benzoate From Phenol And Benzoyl Chloride?
Phenol reacts with Benzoyl chloride in the presence of aqueous
Solution. The correct option is A Phenyl benzoate. Suggest Corrections. 35. Similar questions. Q. Which one of the following product formed when the reaction of phenol with benzoyl chloride in the presence of alkali takes place? Q. Toulene reacts with Cl2 in BYJU’S
Experiment 10 Preparation of the benzoate of phenol.
Many phenols yield crystalline benzoyl derivatives with benzoyl chloride in the presence of sodium hydroxide (Schötten-Baumann method). Mechanism. Procedure: To the phenol (0.5 g) is added 5% sodium The Department of Chemistry, UWI
Benzoylation of phenol with benzoyl chloride in the presence
Benzoylation of phenol with benzoyl chloride in the presence of dilute `NaOH` gives phenyl benzoate. This reaction is an example of. YouTube
The reaction of phenol with benzoyl chloride to give
JEE Main 2013: The reaction of phenol with benzoyl chloride to give phenyl benzoate is known as: (A) Claisen reaction (B) Schotten-Baumann reaction (C Tardigrade
Other Reactions of Phenol – Chemistry LibreTexts
The phenoxide ion reacts more rapidly with benzoyl chloride than the original phenol does, but even so you have to shake it with benzoyl chloride for about 15 Chemistry LibreTexts
some more reactions of phenol – chemguide
In order to get a reasonably quick reaction with benzoyl chloride, the phenol is first converted into sodium phenoxide by dissolving it in sodium hydroxide solution. The chemguide
chemguide: CIE A level chemistry support: Learning outcome
In making phenyl benzoate from phenol and benzoyl chloride, the phenol is made into a better nucleophile by reacting it with sodium hydroxide solution to produce phenoxide chemguide
17.10: Reactions of Phenols – Chemistry LibreTexts
explain why phenols and phenoxide ions are very reactive towards electrophilic aromatic substitution (see Section 16.4 of the textbook). write an equation to illustrate the oxidation of a phenol or an arylamine to a Chemistry LibreTexts
preparation of esters – chemguide
The phenoxide ion reacts more rapidly with benzoyl chloride than the original phenol does, but even so you have to shake it with benzoyl chloride for about 15 minutes. chemguide
22.4: Preparation of Phenols: Nucleophilic Aromatic
For example, chlorobenzene reacts with sodium hydroxide solution at temperatures around \(340^\text{o}\) and this reaction was once an important commercial process for the Chemistry LibreTexts
Preparation Of Phenyl Benzoate//Phenol Derivative//Organic Chemistry Lab
Benzoylation Of Phenol With Benzoyl Chloride In The Presence Of Dilute `Naoh` Gives Phenyl Benzoate.
Synthesis Of Phenyl Benzoate From Phenol# Schotten Baumann Reaction
| Reaction Of Phenol With Acetyl Chloride \U0026 Benzoyl Chloride | Esterification | Class 12 |
Synthesis Of Phenyl Benzoate
Link to this article: reaction of phenol with benzoyl chloride to give phenyl benzoate.
See more articles in the same category here: blog https://countrymusicstop.com/wiki
