How do you treat antral pseudocyst?
It’s a two-step process. First, the pseudocyst is removed. Then, after a few months for healing, a second step is done to rebuild the floor of the sinus.
This procedure is called “two-stage” because it involves two separate surgeries. The first surgery removes the pseudocyst, and the second surgery is done to rebuild the floor of the sinus. This two-stage approach helps the body heal properly and minimizes the risk of complications.
Here’s a bit more detail on why this two-stage approach is often preferred for antral pseudocysts.
First Step: Removing the Pseudocyst – The initial surgery focuses on carefully removing the pseudocyst from the maxillary sinus. This step is crucial to address the primary issue and provide space for the sinus floor to be rebuilt in the next stage.
Second Step: Rebuilding the Sinus Floor – After several months, the body has had time to heal from the initial surgery. The second step, called maxillary sinus floor augmentation, involves adding bone graft material to rebuild the floor of the sinus. This rebuilds the bone structure and helps restore the sinus to its normal function.
This two-stage process allows for controlled healing and helps prevent complications. It provides a solid foundation for the rebuilt sinus floor.
Important Note: The specific treatment plan for an antral pseudocyst will depend on the individual case. You should discuss any potential treatment options with your healthcare provider to determine the best approach for your situation.
How do you treat a maxillary antrum cyst?
So, if your doctor decides that your cyst needs to be removed, they’ll likely use a minimally invasive procedure called endoscopic sinus surgery. This is a really good option because it’s usually quick and doesn’t involve a big incision. There are two main ways to remove the cyst using this technique:
Enucleation: This is where the entire cyst is carefully removed without being punctured or broken open. Think of it like gently peeling a fruit.
Curettage: This method uses a specialized tool that looks like a loop to scoop out the contents of the cyst.
The good news is that most people find the recovery after surgery to be really easy. They report very little discomfort or pain.
Let’s delve a little deeper into what happens during endoscopic sinus surgery:
First, your doctor will numb the area around your nose and sinuses. You’ll be awake during the procedure, but you won’t feel anything. They’ll then use a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope that has a tiny camera on the end. This allows them to get a clear view inside your sinuses.
The endoscope also has tiny instruments that your doctor can use to remove the cyst. They’ll work carefully to avoid damaging the surrounding tissue.
After the surgery, you’ll be given medication to help with any pain or swelling. You’ll also need to keep your nose clean and avoid blowing your nose for a few days. Your doctor will give you detailed instructions to follow.
Most people can go back to their normal activities within a week or two after the surgery.
Remember, it’s crucial to talk to your doctor about any concerns you have about the surgery. They’ll answer your questions and make sure you understand the entire process.
What is a pseudocyst of the maxillary antrum?
You might be wondering how these cysts form. Well, fluid can build up under the periosteum, the thin membrane that covers the bone of the maxillary sinus. This buildup of fluid pushes the antral lining away from the sinus floor, creating the characteristic dome-shaped structure you see on X-rays.
While the word “cyst” might sound scary, maxillary retention cysts are actually not true cysts. They don’t have a lining or contain any infectious material. They’re more like a pocket of fluid that forms in the maxillary sinus.
The good news is that these cysts are usually harmless and don’t cause any symptoms. They’re often discovered during routine dental checkups. However, in some cases, they can become large enough to press on surrounding structures, leading to pain or discomfort. If you experience any symptoms related to a maxillary retention cyst, it’s best to consult with a dentist or oral surgeon to discuss treatment options.
Do maxillary sinus cysts need to be removed?
Smaller maxillary sinus cysts can sometimes go away on their own. However, larger cysts or those causing symptoms often require treatment. Surgery, either through curettage or maxillary sinusectomy, is usually the preferred method for removing these cysts.
Here’s a bit more about those surgical options:
Curettage: This involves carefully scraping away the cyst lining. It’s often done when the cyst is small and located in a specific area of the sinus.
Maxillary sinusectomy: This procedure is used for larger cysts or those that are more widespread within the sinus. It involves making a small opening in the sinus to access the cyst and remove it.
The decision of whether or not to remove a maxillary sinus cyst is based on a few factors, including:
The size of the cyst: Larger cysts are more likely to cause problems and may need to be removed.
The presence of symptoms: If the cyst is causing pain, pressure, or other symptoms, it may be recommended for removal.
The location of the cyst: Cysts located in certain areas of the sinus may be more likely to cause complications.
It’s important to remember that every case is different. Your doctor will assess your specific situation and recommend the best course of action for you. They will also discuss the potential risks and benefits of each treatment option.
Always feel free to ask your doctor any questions you have about your condition. They are there to help you understand your options and make informed decisions about your health.
What is the treatment for a pseudocyst?
Drainage involves removing the fluid from the pseudocyst. This can be done through a procedure called percutaneous drainage. During percutaneous drainage, a thin tube (catheter) is inserted into the pseudocyst through a small incision in your abdomen. The tube is guided using imaging, such as ultrasound or CT scan, to ensure it’s placed accurately. The fluid is then drained out of the cyst.
Another way to drain a pseudocyst is through endoscopic drainage. This procedure involves inserting an endoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a camera attached, into your digestive tract. The endoscope is guided to the pseudocyst, and a small incision is made in the cyst wall. A drainage tube is then inserted into the cyst, allowing the fluid to drain.
Both percutaneous and endoscopic drainage are minimally invasive procedures that are typically performed under sedation. They are generally safe and effective, but there are potential risks involved, such as infection or bleeding. Your doctor will discuss these risks with you before the procedure.
Drainage is often successful in treating pseudocysts, but in some cases, the cyst may come back. If the cyst recurs, your doctor may recommend another drainage procedure or other treatment options, such as surgery.
Can a pseudocyst be removed?
Endoscopic drainage is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope. The endoscope is inserted into the body through a small incision and guided to the pseudocyst. A small tube is then inserted into the pseudocyst, allowing the fluid to drain out. The fluid can be drained into the stomach, intestines, or a drain placed outside the body.
Surgery may be needed if endoscopic drainage is not successful, or if the pseudocyst is too large or complex to be treated with endoscopy. Surgery involves removing the pseudocyst or part of it, and sometimes involves stitching up the lining of the pancreas to help prevent the pseudocyst from coming back.
Pseudocysts can be a serious condition, but treatment is often successful. If you are concerned about a pseudocyst, be sure to see a doctor. They can help determine the best course of treatment for you.
See more here: How Do You Treat A Maxillary Antrum Cyst? | Maxillary Sinus Antral Pseudocyst Treatment
Are antral pseudocysts common during maxillary sinus augmentation (MSA)?
This article aims to review the current research on MSA in patients with antral pseudocysts. Our goal is to see if there’s a general agreement on how to handle them during MSA.
Antral pseudocysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop in the maxillary sinus. They’re often asymptomatic, meaning they don’t cause any pain or discomfort. However, they can sometimes get infected, leading to sinusitis.
During MSA, a surgeon might encounter an antral pseudocyst. If so, they’ll need to decide whether to remove it or leave it alone. The decision depends on the size and location of the pseudocyst and the overall goals of the procedure.
If the pseudocyst is small and not causing any problems, the surgeon might choose to leave it in place. However, if the pseudocyst is large or in a location that could interfere with the implant placement, it might need to be removed.
Removing an antral pseudocyst during MSA is usually straightforward. The surgeon will carefully drain the fluid and then remove the cyst wall. This procedure is typically done with a small incision in the sinus lining.
The decision to remove or leave an antral pseudocyst during MSA is ultimately up to the surgeon. They will consider your individual needs and the specifics of your situation to make the best decision for you.
Can crestal sinus augmentation be performed in the presence of antral pseudocyst?
Crestal sinus augmentation is a procedure used to increase the height of the upper jawbone, which is essential for placing dental implants. This is typically done when there’s insufficient bone to support an implant. It involves raising the sinus membrane, also known as the Schneiderian membrane, and grafting bone material into the space created.
Now, an antral pseudocyst is a fluid-filled sac located in the maxillary sinus. While it sounds scary, it’s usually harmless and doesn’t cause symptoms. However, it can sometimes interfere with dental procedures like crestal sinus augmentation.
Can crestal sinus augmentation be done in the presence of an antral pseudocyst? The answer is yes, but it requires careful planning and consideration. Here’s why:
The pseudocyst might need to be removed or drained before the augmentation procedure. This is because it can affect the stability of the bone graft and potentially lead to complications.
The presence of the pseudocyst might increase the risk of complications during the procedure. This is because it can make the sinus membrane more fragile and prone to tearing.
The pseudocyst might need to be monitored after the augmentation procedure. This is because it can sometimes return after surgery.
So, in short, crestal sinus augmentation can be performed in the presence of an antral pseudocyst, but it’s crucial to consult with a qualified oral surgeon or periodontist to determine the best course of action. They can evaluate your specific case and advise you on the risks and benefits of the procedure.
In addition to the above, here’s a deeper dive into the considerations:
The size and location of the pseudocyst are crucial factors. A small pseudocyst located away from the planned augmentation site might not require any special attention. However, a large pseudocyst, especially one that’s close to the planned bone graft, will need careful management.
The surgeon’s experience and expertise are essential. A skilled surgeon will be able to navigate the challenges posed by the pseudocyst and minimize the risk of complications.
Post-operative care and monitoring are vital. Regular check-ups will ensure that the pseudocyst doesn’t return and that the bone graft is healing properly.
It’s also important to understand that crestal sinus augmentation isn’t the only option when dealing with an antral pseudocyst. Sometimes, simply observing the pseudocyst might be the best approach, especially if it’s small and asymptomatic. In other cases, a lateral sinus lift might be a better choice. This involves creating an access window in the lateral wall of the sinus, which may be less challenging in the presence of a pseudocyst.
The best approach for your specific situation will depend on various factors. Don’t hesitate to discuss your concerns and options with your oral surgeon or periodontist. They are the best resource to help you make informed decisions about your dental health.
What is antral pseudocyst (AP)?
Think of it like a tiny, fluid-filled sac, and it’s not a real cyst. A true cyst has its own lining, but an AP doesn’t. It’s more like a small pocket of fluid that’s formed within the sinus.
You might be wondering why these APs appear. It’s usually due to a bit of inflammation or irritation in the lining of the maxillary sinus. This inflammation can be caused by various factors, like infections, allergies, or even just changes in pressure.
It’s important to note that APs are generally harmless and don’t cause any symptoms. They usually don’t need any treatment and often go away on their own.
However, in rare cases, an AP might become a bit larger and cause some discomfort, like pressure or pain in the face. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s a good idea to see a doctor to rule out any other potential causes. They can examine the situation and determine if any further investigation or treatment is necessary.
What is a treatment algorithm for antral pseudocyst (AP)?
Think of a treatment algorithm like a decision-making flowchart. It helps determine the best approach for a particular case. By following this algorithm, practitioners can consider the size, location, and symptoms of the AP, along with the patient’s overall health and preferences, to choose the most appropriate course of action. It’s essentially a roadmap to guide practitioners through the various treatment options available.
For example, if a patient has a small, asymptomatic AP, observation might be the recommended approach. However, if the cyst is causing symptoms like facial pain or pressure, or if it’s large enough to interfere with the planned MSA procedure, then surgical intervention may be necessary.
Here’s a simplified example of how a treatment algorithm for AP might work:
1. Identify the presence of an AP: This usually involves a CT scan or other imaging studies.
2. Assess the size and location of the AP: Is it small and isolated, or large and affecting the maxillary sinus?
3. Evaluate for symptoms: Are there any signs of discomfort or pain associated with the AP?
4. Consider the planned procedure: Is an MSA planned, and if so, is the AP interfering?
5. Determine the appropriate treatment: Depending on the answers to the above questions, the options might include:
Observation: If the AP is small and asymptomatic, monitoring its size and symptoms over time might be sufficient.
Conservative management: This could involve medication to alleviate pain or pressure, or nasal irrigation to clear the sinus cavity.
Surgical intervention: If the AP is causing symptoms, or if it’s affecting the planned MSA, surgical removal might be necessary. This could involve endoscopic sinus surgery or other minimally invasive approaches.
The treatment algorithm serves as a structured framework to guide practitioners in making informed decisions, leading to the most effective and appropriate treatment for each patient. It helps ensure that the treatment plan is tailored to the individual needs of the patient and their specific situation.
See more new information: countrymusicstop.com
Maxillary Sinus Antral Pseudocyst Treatment: What You Need To Know
Hey there, so you’re dealing with a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst? I get it, it can be a bit confusing, but don’t worry, I’m here to break it down for you.
First things first, let’s get a handle on what a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst actually is.
Imagine your sinuses, those air-filled spaces in your skull. Well, a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst is basically a fluid-filled sac that pops up in your maxillary sinus, the one right above your teeth. It’s not a true cyst, though, because it doesn’t have a lining like a regular cyst.
Now, the good news is that most of the time, these pseudocysts are harmless. They usually don’t cause any symptoms, and they often go away on their own.
But what if you’re experiencing symptoms?
That’s when things get a little more interesting, and we need to talk about treatment.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Let’s be real, if you’re having symptoms related to your maxillary sinus like:
Facial pain
Pressure
Headache
Nasal congestion
Discharge from your nose
It’s a good idea to see your doctor or an ENT specialist.
How Do They Diagnose a Maxillary Sinus Antral Pseudocyst?
So, how does your doctor figure out what’s going on? Usually, they’ll do a physical exam, ask about your symptoms, and maybe do some imaging tests. The most common imaging test is a CT scan of your sinuses.
So, What About Treatment?
Now we’re getting to the meat of the matter. The treatment for a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst really depends on whether or not you have symptoms.
No Symptoms?
* Chill out. Your doctor will probably just keep an eye on things, and you might not need any treatment.
Symptoms?
* If you’re dealing with those pesky symptoms, your doctor might recommend conservative treatment, which could involve things like:
Nasal corticosteroids
Decongestants
Antibiotics
Saline rinses
Surgery (in rare cases)
Let’s Talk About Surgery
Okay, surgery isn’t always the first option, but sometimes it’s needed. This is usually if other treatments haven’t worked, or if the pseudocyst is really large and causing a bunch of problems.
Surgery to remove a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst is typically done under general anesthesia. Your surgeon will make a small incision in your nose or cheek, and then they’ll carefully remove the pseudocyst from your maxillary sinus.
Recovery from surgery usually takes a few days, and you’ll likely need to avoid strenuous activity for a week or two.
Can a Maxillary Sinus Antral Pseudocyst Come Back?
I know what you’re thinking, “What if it comes back?” Well, it’s possible, but not super common. Sometimes, it can reappear, and your doctor might suggest a repeat surgery.
Maxillary Sinus Antral Pseudocyst FAQs
Here are some common questions about maxillary sinus antral pseudocysts that you might be wondering:
1. What causes a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst?
While the exact cause is a bit of a mystery, we know that they’re often linked to inflammation in the sinuses, which could be triggered by things like:
Allergies
Infections
Sinusitis
Trauma
Dental procedures
2. Are maxillary sinus antral pseudocysts dangerous?
Most of the time, no. They’re typically harmless and go away on their own. However, if they get large enough or cause symptoms, they can be a bit of a nuisance.
3. How can I prevent a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst?
Unfortunately, there’s no foolproof way to prevent a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst, but here are some things you can do:
Manage your allergies.
Treat sinus infections promptly.
Practice good oral hygiene.
Avoid dental procedures that could put your sinuses at risk.
4. What if I have a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst and I’m pregnant?
That’s a great question. If you’re pregnant and you develop a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst, your doctor will likely take a conservative approach, using things like nasal corticosteroids or saline rinses to manage symptoms. They’ll usually avoid surgery until after you deliver the baby.
5. What’s the long-term outlook for someone with a maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst?
The good news is that the long-term outlook is usually quite good. Most maxillary sinus antral pseudocysts are harmless and go away on their own. Even if you need surgery, the success rate is high, and you can expect a full recovery.
Let me know if you have any more questions. I’m here to help!
A Reliable Surgical Procedure for Sinus Floor Augmentation with
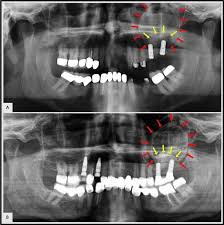
An antral pseudocyst (AP) is a common well-defined ‘dome-shaped’ faintly radiopaque lesion of the maxillary sinus, and usually does not require treatment in asymptomatic patients. National Center for Biotechnology Information
A Clinical Approach for the Removal of a Large Antral
For a large benign lesion within the maxillary sinus, such as an antral pseudocyst, maxillary sinus floor augmentation is more commonly performed using a two-stage approach. This National Center for Biotechnology Information
Comprehensive review and proposed treatment algorithm
Antral Pseudocysts (AP) are fairly common lesions of the maxillary sinus and may often be encountered during Maxillary Sinus Augmentation (MSA). The objective of ScienceDirect
Are mucous retention cysts and pseudocysts in the maxillary
Mucous retention cysts and pseudocysts of the maxillary sinus are benign lesions present in up to 13% of adult patients. Different surgical approaches for sinus lift National Center for Biotechnology Information
Maxillary sinus augmentation in the presence of antral
The “antral pseudocyst,” a term used to describe a sessile soft tissue elevation on the floor of the maxillary sinus, is caused by the accumulation of ScienceDirect
Maxillary sinus augmentation in the presence of antral
The maxillary sinus augmentation procedure has been routinely performed with predictable results, and is an acceptable, safe modality for bone augmentation, providing a base for endosseous oooojournal.net
A Reliable Surgical Procedure for Sinus Floor Augmentation with
An antral pseudocyst (AP) is a common well-defined ‘dome-shaped’ faintly radiopaque lesion of the maxillary sinus, and usually does not require treatment in PubMed
Antral pseudocysts | Registered Dental Hygienists
Antral pseudocysts, on the other hand, are not true cysts and are not often associated with clinical symptoms. Antral pseudocysts arise from the floor of the maxillary sinus and form beneath the mucous Registered Dental Hygienist (RDH) Magazine
Maxillary sinus augmentation in the presence of antral
A pseudocyst of the maxillary sinus is not a contraindication for sinus augmentation. The low frequency of sinus membrane perforation and postsurgery sinusitis make the oooojournal.net
Comprehensive review and proposed treatment algorithm
Antral Pseudocysts (AP) are fairly common benign lesions of the maxillary sinus. As its name suggests, an AP is not histologically a true cyst as it is not ScienceDirect
Maxillary Sinus Retention Cyst Treatment \U0026 Simultaneous Sinus Lift
Antral Pseudocyst / Benign Mucosal Cyst Of Maxillary Antrum
Large Maxillary Sinus Cyst Enucleated By Intra Oral Approach
Maxillary Sinus Diseases | Sinusitis | Oro-Antral Communication/Fistula | Caldwell-Luc Procedure
Maxillary Sinus Cyst Removal
Link to this article: maxillary sinus antral pseudocyst treatment.
See more articles in the same category here: blog https://countrymusicstop.com/wiki
